Definition :
- allows an attacker to inject javascript code into the page
- Code is executed when page loads
- Code is executed on the client side not server side cause javascript is a client side language
Types :
1. Stored XSS :
This vulnerability occurs when your javascript code gets stored in the databse permanently, which means it will be executed if anyone clicks on that link (which looks like a normal link)
2. Reflected XSS :
This vulnerability is not stored in the database , which means it only gets executed if target clicks on a custom link
3. DOM based XSS :
This is when when the javascript is run and executed in the client machine without even interacting web sites, which is useful cause there are no server side filters
Discovery :
If you by chance see your text being executed / displayed in any part of website or somewhere in ” inspect element ” and ^F to search ur injection then It may be vulnerable
Exploitation :
The method of exploitation is the same for Reflected / Stored or DOM but their internal working is different
Step 1 : Simple HTML injection
This is less dangerous than XSS but still needs to be reported Injecting HTML tags and if it works then most probably it in vulnerable to XSS, something like this
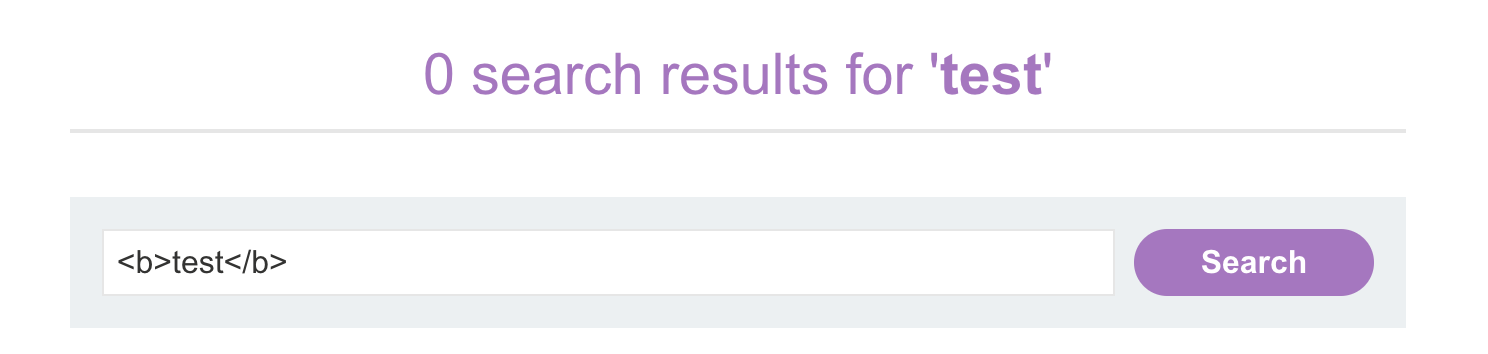
Step 2 : Simple XSS injections
Similar, but Javascript code is used instead
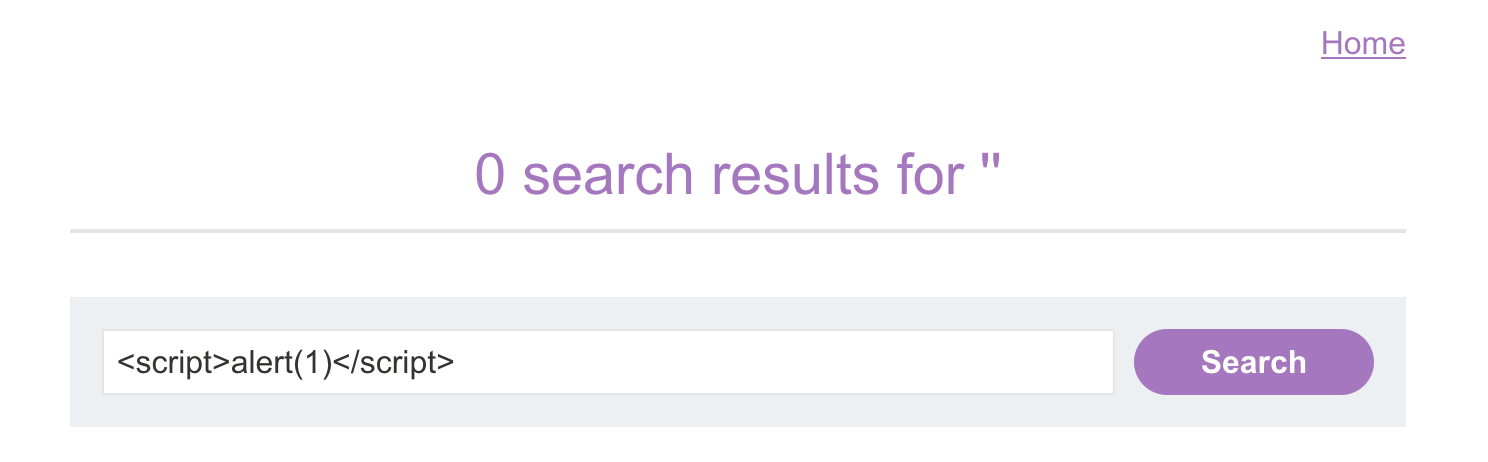
Important Checks :
Usually inspect element to see under which <tag> your code is getting executed and learn about that tag and then google - Can I run javascript in that tag?
Also try to close the tag and comment the rest if necessary
IF XSS in link tag (<a href) :
Like here :
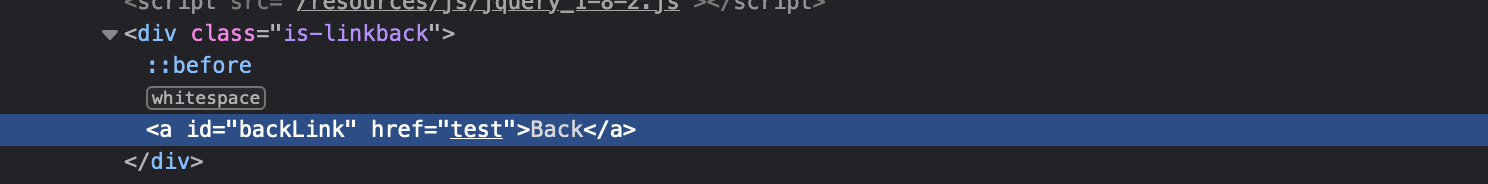
then we can inject javascript code like javascript:alert(2):
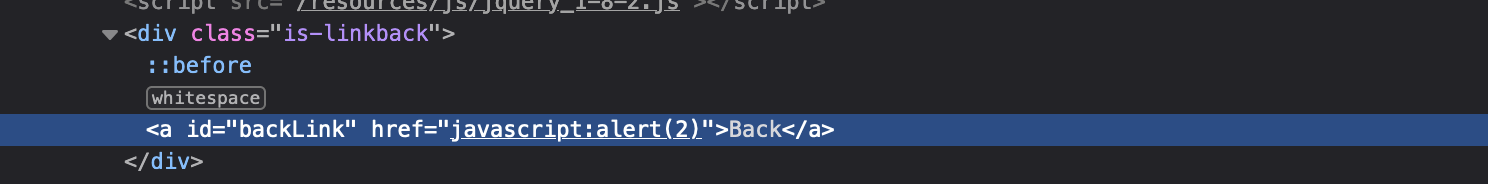
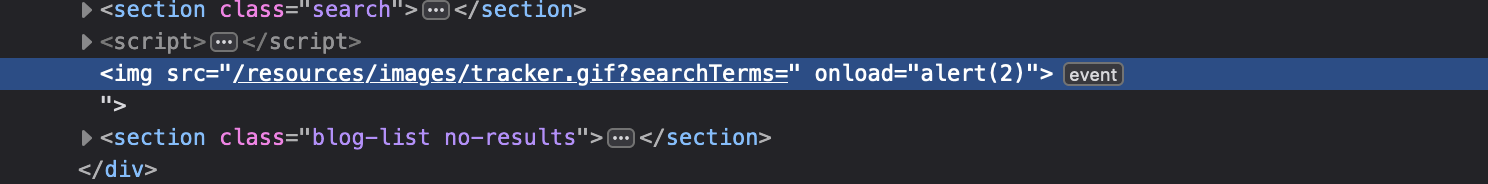
IF XSS in image tag <img:
then we can inject code like " onload=alert(2)> :
IF XSS in script tag <script:
Its a lot easier, just inspect element and try to bypass everything like :
- Add “ to end their “
- Add // at the end to comment rest stuff
- Add ; to end a sentence and start a new one
IF XSS in Drop down menu :
-
using Burp we find 2 parameters and

-
1 parameter is already shown in URL Like :
?productId=6 -
Then Inject the value of both first and second parameter ( Here 2nd parameter was injectable ) So change the URL the same way it was in Burp wrt 1st parameter like this :
Note : make sure to inspect element and see if everythong is alreight in <option> tag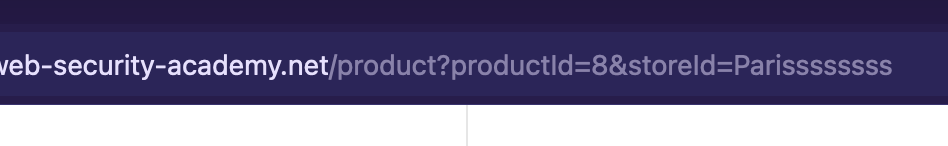 And If we get the change like this :
And If we get the change like this :
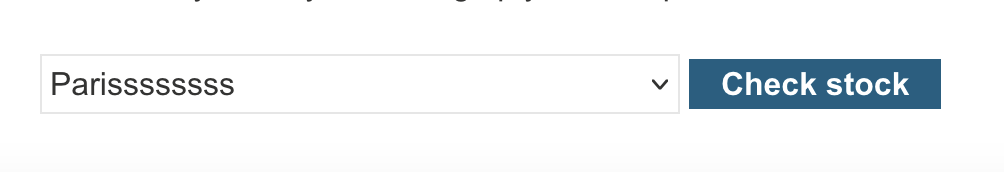
-
Inject JS code like
?productid=8&storeid=<script>alert(1)</script>
Step 3 : Check Technology
Check their JS Framework using Wappalyzer and then Google : (Framework) XSS cheatsheet
Step 4 : Bypassing Some Filters
If they are using backticks (`) around input :
Their code is like :
var message ='Your text is "example_text"`;Our injection : <span style=“color:cyan”;>${alert(1)} ⇒ which is a Javascript Code to run inside backticks
Final Code :
var messege = `Your text is "${alert(1)}"`; If they are using \ to nullify ' :
Normally when we inject : <span style=“color:cyan”;>‘;alert(1);//
The code becomes : var message = '\<span style=“color:cyan”;>‘;alert(1);//;
which Nullifies our ' because of \ So we add a \ ourselves before to nullify it
Injection : <span style=“color:cyan”;>‘;alert(1);//
Final Code : var message = '\<span style=“color:cyan”;>‘;alert(1);//;
Smarter Way to bypass their \ :
Websites Usually automatically put a \ before ' to stop them from abusing it but when we use our \ they use \\ to nullify so there is a better way to write ' that is :
'
'
&apos
etc. ask chatgpt
Step 5 : Weird Advance bypassing
If normal HTML and XSS injection tags are all getting filtered then :
Try to inject a tag which does not exist Ex : <Bruh>Text</Bruh> and If it gets added in the code like this :

Then It is vulnerable and add this : <Bruh onfocus=alert(1) tabindex=1>text</Bruh>
If it gets executed then clicking on the “test” will trigger alert
Step 6 : Weird Advance Bypassing using Intruder
Go through the cheatsheet here and test all tags and events using BurpSuite Intruder
Ex : <demo_tag1%20demo_event1=alert(1)>test
Note : %20 means space